Last update: July 19, 2015
JPEG
JPEG (file extension.jpg) is a commonly used method of lossy compression for digital images. The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality.
The term JPEG is an acronym for the Joint Photographic Experts Group, which was organized in 1986 and created the first standard in 1992. JPEG uses a lossy form of compression based on the discrete cosine transform (DCT). The method lossy means that some original image information is lost and cannot be restored, possibly affecting image quality.
Progressive JPEG
The interlaced Progressive JPEG format compresses data in multiple passes of progressively higher detail. This is ideal for large images that will be displayed while downloading over a slow connection, allowing a reasonable preview after receiving only a portion of the data.
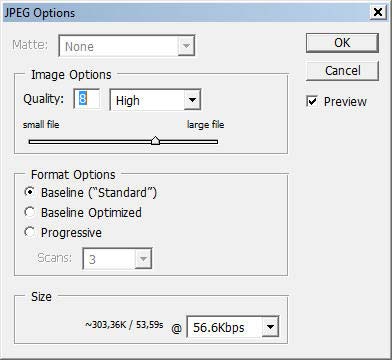
Standard Photoshop CS2 JPEG Save as options
JPEG-HDR
JPEG-HDR is an extension to the standard JPEG image file format allowing it to store high dynamic range images. It was created by Greg Ward and Maryann Simmons as a way to store high dynamic range images inside a standard JPEG file.
JPEG-XR
JPEG XR is a still-image compression standard and file format for continuous tone photographic images, based on technology originally developed and patented by Microsoft under the name HD Photo. It supports both lossy and lossless compression and is supported in Internet Explorer 9 and alter versions. Today there are not yet cameras that shoot photos in the JPEG XR (.JXR) format.
Lossless JPEG
An optional lossless mode was defined in the JPEG standard in 1993, using a completely different technique as the lossy JPEG standard. The lossless coding process employs a simple predictive coding model called differential pulse code modulation (DPCM). Lossless JPEG has some popularity in medical imaging (DICOM), and is used in DNG and some digital cameras to compress raw images, but otherwise was never widely adopted.
Today the term lossless JPEG is usually used as umbrella term to refer to all lossless image compression schemes including JPEG-LS and JPG 2000.
JPEG-LS
JPEG-LS is a lossless/near-lossless compression standard for continuous-tone images with the official designation ISO-14495-1/ITU-T.87. Part 1 of this standard was finalized in 1999. Besides lossless compression, JPEG-LS also provides a lossy mode (“near-lossless”) where the maximum absolute error can be controlled by the encoder. The filename extension is .jls. Compression for JPEG-LS is generally much faster than JPEG 2000 and much better than the original lossless JPEG standard. The JPEG-LS standard is based on the LOCO-I algorithm (LOw COmplexity LOssless COmpression for Images) developed at Hewlett-Packard Laboratories.
JPEG 2000
JPEG 2000 is an image compression standard and coding system defined in 2000 with the intention of superseding the original discrete cosine transform-based JPEG standard with a newly designed, wavelet-based method. The standardized filename extension is .jp2 or .jpx for the extended part-2 specification. JPEG 2000 is not widely supported in web browsers and therefore not generally used on the Internet. JP2 includes mandatory metadata such as information about an image’s color space. It handles alpha transparency and 16-bit color mode.
Photoshop plugins : JPEG-LS, JPEG-XR, JPEG-2000
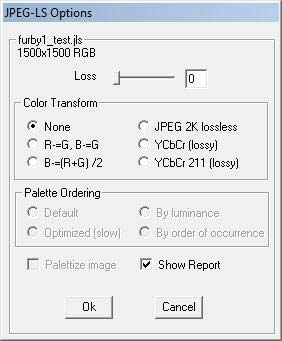
Photoshop CS2 JPEG-LS plugin by HP
HP offers a copyrighted Photoshop plugin for JPEG-LS. Additional informations about JPEG-LS source code are available at the Wayback Archive Webpage of Aleks Jakulin.
A free JPEG 2000 (j2k) plugin for Photoshop is provided by fnord software, a small software boutique in San Francisco, creating graphics software primarily for Macintosh computers. fnord software provides also a SuperPNG plugin for Adobe Photoshop and a WebM plugin for Adobe Premiere.
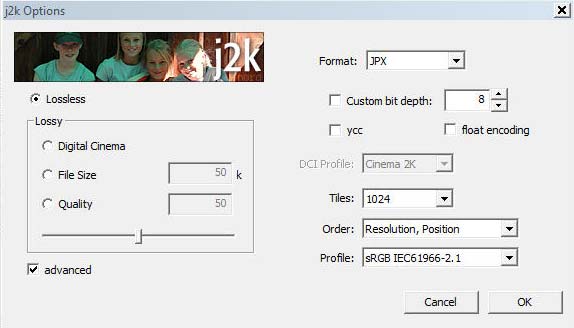
JPEG 2000 plugin from fnor software in Photoshop CS2
The advanced features are not working as expected in my Photoshop CS2 version.
Microsoft provides a Photoshop plugin for JPEG-XR
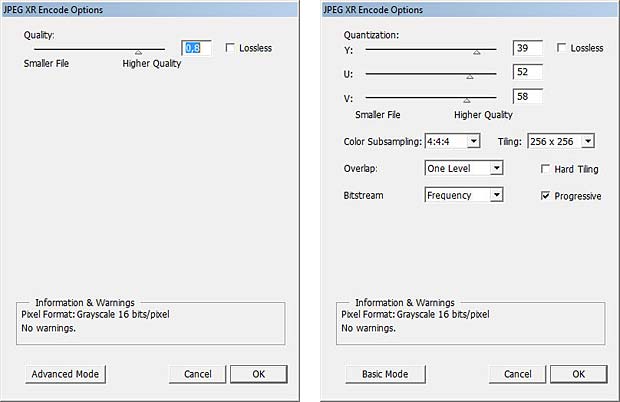
JPEG-XR plugin from Microsoft in Photoshop CS2
.
