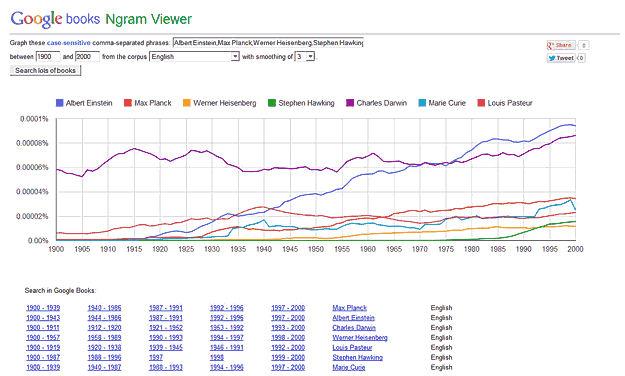
Last update : August 6, 2013
Joy Paul Guilford, a United States psychologist, designed in 1955 a model of intelligence, based on factor analysis. In the Guilfords Structure of Intellect (SI), all mental abilities are conceptualized within a three-dimensional framework. There are three features of intellectual tasks: the content, or the type of information; the product, or the form in which the information is represented; and the operation, or type of mental activity performed.
These 5 x 6 x 6 = 180 mental abilities are listed below :
Content features in the Guilfords Structure of Intellect
Five content dimensions (broad areas of information to which the human intellect applies operations) :
- Visual : information perceived through seeing
- Auditory : information perceived through hearing
- Symbolic : information perceived as symbols or signs that stand for something else (arabic numerals, letters of an alphabet, musical and scientific notations)
- Semantic : concerned with verbal meaning and ideas
- Behavioral : information perceived as acts of people
Product features in the Guilfords Structure of Intellect
Six products, in increasing complexity :
- Units : single items of knowledge
- Classes : sets of units sharing common attributes
- Relations : units linked as opposites or in associations, sequences, or analogies
- Systems : multiple relations interrelated to comprise structures or networks
- Transformations : changes, perspectives, conversions, or mutations to knowledge
- Implications : predictions, inferences, consequences, or anticipations of knowledge
Operation features in the Guilfords Structure of Intellect
Six operations (general intellectual processes) :
- Cognition : the ability to understand, comprehend, discover, and become aware of information
- Memory recording : the ability to encode information
- Memory retention : the ability to recall information
- Divergent production : the ability to generate multiple solutions to a problem; creativity
- Convergent production : the ability to deduce a single solution to a problem; rule-following or problem-solving
- Evaluation : the ability to judge whether or not information is accurate, consistent, or valid
Guilford’s original model was composed of 120 components, because he combined Visual and Auditory content in a common Figural Content and he combined Memory Recording and Memory Retention in a common Memory Operation. Guilford’s model is an open system such that it allows for newly discovered categories to be added in any of the three directions.
Guilfords Structure of Intellect has few supporters today, but Joy Paul Guilford is considered as one of the founders of the Psychology of Creativity. He emphasized the distinction between convergent and divergent thinking. In 1976 he introduced the developed model of Divergent Thinking as the main ingredient of creativity. Guilford appointed the following characteristics for creativity :
- Fluency : the ability to produce great number of ideas or problem solutions
- Flexibility : the ability to simultaneously propose a variety of approaches to a specific problem
- Originality : the ability to produce new, original ideas
- Elaboration : the ability to systematize and organize the details of an idea in a head and carry it out
Peter Nilsson uses the following example to measure the creativity of people based on Guilford’s concept of divergent production :
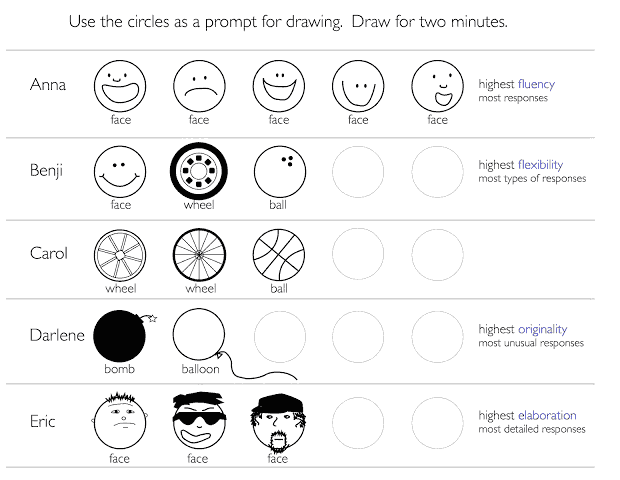
Creativity Measurement
Links to additional informations about the Guilfords Structure of Intellect and about the measurement of creativity are provided in the following list :