Last update : August 6, 2013
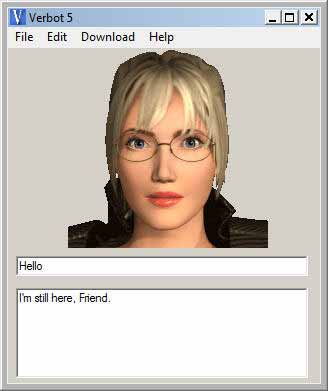
Verbot 5
Verbots (Verbally Enchanted Software Robots) is a popular chatterbot program and Artificial Intelligence Software Development Kit (SDK) for the Windows platform and for the web, created by Dr. Michael Mauldin and Peter Plantec.
Some milestones of the history of verbots are presented hereafter :
- 1989 : TinyMUD Gloria
- 1990 : TinyMUD Julia
- 1991 : participation of Julia in the first Loebner Prize contest
- 1994 : chatterbot Julia
- 1997 : creation of Virtual Personalities, Inc.
- 2000 : production release of the virtual human interface Sylvie
- 2004 : release of the Verbot 4 version
- 2006 : start of Verbots Online
- 2010 : relase of the Verbot 5 version
Version 4 of verbots was based on MS Agent which has been discontinued by Microsoft in Windows 7. A properties viewer of MS agents has been created by AbhiSoft Technologies. A related scripting software has been developed by the same company who also provides a file repository for MS Agents.
Version 5 of verbots uses characters made up of 22 SAPI5 viseme groups and animations. The Conversive Character Studio Application allows you to easily create your own talking characters that are compatible with Verbots and VerbotsOnline using high-quality SAPI 5 tts voices. Conversive characters are defined in a .css file in xml format. Sample visemes are available at the verbots wiki website. Animations are a collection of frames which are displayed on the screen in sequence.
The different verbots file types are :
- ckb : Compiled KnowledgeBase
- csv : Comma Separated Values
- vkb : Verbot KnowledgeBase
- vrp : Verbot Replacement Profile
- vsn : Verbot Synonyms
The templates to create the Verbots brain are the following :
- My answers
- My Knowledge Bases
- My Design
- Install
In the Online version you can browse the chat logs, manage your account and list your bot in the online directory. Several tags are available to commande the Verbot. A Verbot editor allows to create and edit the different templates. KnowledgeBases are created from a collection of Rules. Rules contain Inputs and Outputs. Rules can be Primary Rules, Child Rules or Virtual Child Rules. Conditionals, variables and regular expressions are further means to set up a personality. Special inputs allow to start and stop animations, embedded C# code modules allows to execute programs, schedue tags allow to trigger time events, commands are used to open web adresses or to run applications.
The Teaching.vkb KnowledgeBase allows new rules to be dynamically added while chatting.
ChatVerbots for IRC and AIM are available as beta versions.
The following tutorials about Verbots are available :
- Creating personalities
- Creating your first rule
- Creating child rules
- Knowledge Base templates and csv files
Communities discussing about verbots are listed below :
Concerning AIML (Artificial Intelligence Markup Language maintained by the Alice Foundation ), verbots don’t comply to this standard. Verbots KB (Knowledge Base) and AIML both are XML based, but the format is different, the working of engine is different, the usability is different.
A free tool to convert AIML files to Verbots KB files is available at the Verbots website.
The Alice Foundation is more active, more dynamic and more professional, compared to the Verbots Community, whereas the Verbots Technology offers some outstanding features.
The Verbots Online Service was closing down at the end of August 2012. Free webhosting for AIML is still available : Pandorabots for AIML. To fully customize your Bot and to give him a Voice (TTS), a paid subscription is required. SitePal.