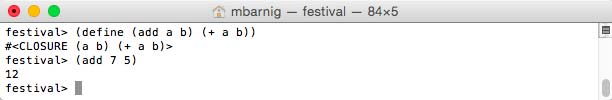
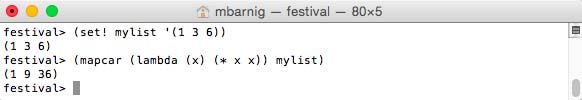
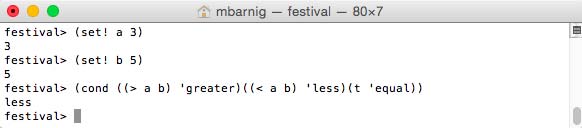
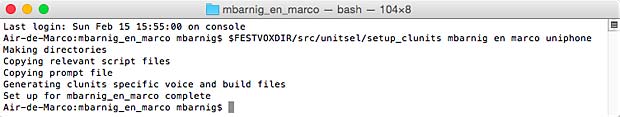
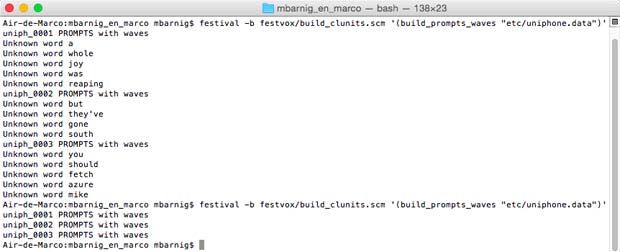
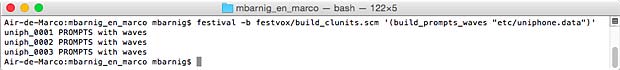
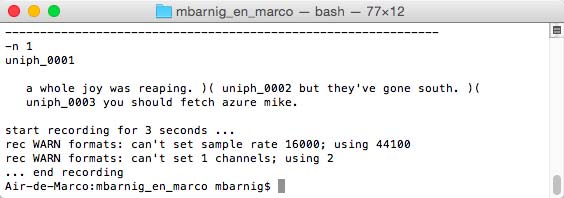
Last update : April 2, 2015
Utterance Definition
In linguistics an utterance is a unit of speech, without having a precise definition. It’s a bit of spoken language. It could be anything from “Baf!” to a full sentence or a long speech. The corresponding unit in written language is text.
Phonetically an utterance is a unit of speech bounded (preceded and followed) by silence. Phonemes, phones, morphemes, words etc are all considered items of an utterance.
In orthography, an utterance begins with a capital letter and ends in a period, question mark, or exclamation point.
In Speech Synthesis (TTS) the text that you wish to be spoken is contained within an utterance object (example : SpeechSynthesisUtterance). The Festival TTS system uses the utterance as the basic object for synthesis. Speech synthesis is the process that applies a set of programs to an utterance.
The main stages to convert textual input to speech output are :
- Conversion of the input text to tokens
- Conversion of tokens to words
- Conversion of words to strings of phonemes
- Addition of prosodic information
- Generation of a waveform
In Festival each stage is executed in several steps. The number of steps and what actually happens may vary and is dependent on the particular language and voice selected. Each of the steps is achieved by a Festival module which will typically add new information to the utterance structure. Swapping of modules is possible.
Festival provides six synthesizer modules :
- 2 diphone engines : MBROLA and diphone
- 2 unit selection engines : clunits and multisyn
- 2 HMM engines : clustergen and HTS
Festival Utterance Architecture
A very simple utterance architecture is the string model where the high level items are replaced sequentially by lower level items, from tokens to phones. The disadvantage of this architecture is the loss of information about higher levels.
Another architecture is the multi-level table model with one hierarchy. The problem is that there are no explicit connections between levels.
Festival uses a Heterogeneous Relation Graph (HRG). This model is defined as follows :
- Utterances consist of a set of items, representing things like tokens, words, phones,
- Each item is related by one or more relations to other items.
- Each item contains a set of features, having each a name and a value.
- Relations define lists, trees or lattices of items.
The stages and steps to build an utterance in Festival, described in the following chapters, are related to the us-english language and to the clustergen voice cmu_us_slt_cg.
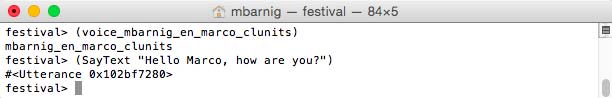
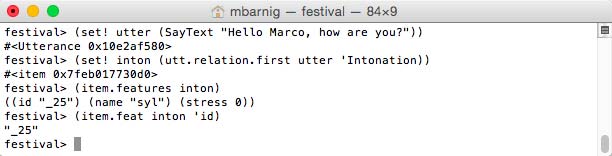
To explore the architecture (structure) of an utterance in Festival, I will analyse the relation-trees created by the synthesis of the text string “253”.
festival> (voice_cmu_us_slt_cg)
cmu_us_slt_cg
festival> (set! utter (SayText "253"))
#<Utterance 0x104c20720>
festival> (utt.relationnames utter)
(Token
Word
Phrase
Syllable
Segment
SylStructure
IntEvent
Intonation
Target
HMMstate
segstate
mcep
mcep_link
Wave)
festival> (utt.relation_tree utter 'Token)
((("253"
((id "_1")
(name "253")
(whitespace "")
(prepunctuation "")
(token_pos "cardinal")))
(("two"
((id "_2")
(name "two")
(pos_index 1)
(pos_index_score 0)
(pos "cd")
(phr_pos "cd")
(phrase_score -0.69302821)
(pbreak_index 1)
(pbreak_index_score 0)
(pbreak "NB"))))
(("hundred"
((id "_3")
(name "hundred")
(pos_index 1)
(pos_index_score 0)
(pos "cd")
(phr_pos "cd")
(phrase_score -0.692711)
(pbreak_index 1)
(pbreak_index_score 0)
(pbreak "NB"))))
(("fifty"
((id "_4")
(name "fifty")
(pos_index 8)
(pos_index_score 0)
(pos "nn")
(phr_pos "n")
(phrase_score -0.69282991)
(pbreak_index 1)
(pbreak_index_score 0)
(pbreak "NB"))))
(("three"
((id "_5")
(name "three")
(pos_index 1)
(pos_index_score 0)
(pos "cd")
(phr_pos "cd")
(pbreak_index 0)
(pbreak_index_score 0)
(pbreak "B")
(blevel 3))))))
festival> (utt.relation_tree utter 'Word)
((("two"
((id "_2")
(name "two")
(pos_index 1)
(pos_index_score 0)
(pos "cd")
(phr_pos "cd")
(phrase_score -0.69302821)
(pbreak_index 1)
(pbreak_index_score 0)
(pbreak "NB"))))
(("hundred"
...
...
(blevel 3)))))
festival> (utt.relation_tree utter 'Phrase)
((("B" ((id "_6") (name "B")))
(("two"
((id "_2")
(name "two")
(pos_index 1)
(pos_index_score 0)
(pos "cd")
(phr_pos "cd")
(phrase_score -0.69302821)
(pbreak_index 1)
(pbreak_index_score 0)
(pbreak "NB"))))
(("hundred"
...
...
(blevel 3))))))
festival> (utt.relation_tree utter 'Syllable)
((("syl" ((id "_7") (name "syl") (stress 1))))
(("syl" ((id "_10") (name "syl") (stress 1))))
(("syl" ((id "_14") (name "syl") (stress 0))))
(("syl" ((id "_19") (name "syl") (stress 1))))
(("syl" ((id "_23") (name "syl") (stress 0))))
(("syl" ((id "_26") (name "syl") (stress 1)))))
festival> (utt.relation_tree utter 'Segment)
((("pau" ((id "_30") (name "pau") (end 0.15000001))))
(("t" ((id "_8") (name "t") (end 0.25016451))))
(("uw" ((id "_9") (name "uw") (end 0.32980475))))
(("hh" ((id "_11") (name "hh") (end 0.39506164))))
(("ah" ((id "_12") (name "ah") (end 0.48999402))))
(("n" ((id "_13") (name "n") (end 0.56175226))))
(("d" ((id "_15") (name "d") (end 0.59711802))))
(("r" ((id "_16") (name "r") (end 0.65382934))))
(("ax" ((id "_17") (name "ax") (end 0.67743915))))
(("d" ((id "_18") (name "d") (end 0.75765681))))
(("f" ((id "_20") (name "f") (end 0.86216313))))
(("ih" ((id "_21") (name "ih") (end 0.93317086))))
(("f" ((id "_22") (name "f") (end 1.0023116))))
(("t" ((id "_24") (name "t") (end 1.0642071))))
(("iy" ((id "_25") (name "iy") (end 1.1534019))))
(("th" ((id "_27") (name "th") (end 1.2816957))))
(("r" ((id "_28") (name "r") (end 1.3449684))))
(("iy" ((id "_29") (name "iy") (end 1.5254952))))
(("pau" ((id "_31") (name "pau") (end 1.6754951)))))
festival> (utt.relation_tree utter 'SylStructure)
((("two"
((id "_2")
(name "two")
(pos_index 1)
(pos_index_score 0)
(pos "cd")
(phr_pos "cd")
(phrase_score -0.69302821)
(pbreak_index 1)
(pbreak_index_score 0)
(pbreak "NB")))
(("syl" ((id "_7") (name "syl") (stress 1)))
(("t" ((id "_8") (name "t") (end 0.25016451))))
(("uw" ((id "_9") (name "uw") (end 0.32980475))))))
(("hundred"
((id "_3")
(name "hundred")
(pos_index 1)
(pos_index_score 0)
(pos "cd")
(phr_pos "cd")
(phrase_score -0.692711)
(pbreak_index 1)
(pbreak_index_score 0)
(pbreak "NB")))
(("syl" ((id "_10") (name "syl") (stress 1)))
(("hh" ((id "_11") (name "hh") (end 0.39506164))))
(("ah" ((id "_12") (name "ah") (end 0.48999402))))
(("n" ((id "_13") (name "n") (end 0.56175226)))))
(("syl" ((id "_14") (name "syl") (stress 0)))
(("d" ((id "_15") (name "d") (end 0.59711802))))
(("r" ((id "_16") (name "r") (end 0.65382934))))
(("ax" ((id "_17") (name "ax") (end 0.67743915))))
(("d" ((id "_18") (name "d") (end 0.75765681))))))
(("fifty"
((id "_4")
(name "fifty")
(pos_index 8)
(pos_index_score 0)
(pos "nn")
(phr_pos "n")
(phrase_score -0.69282991)
(pbreak_index 1)
(pbreak_index_score 0)
(pbreak "NB")))
(("syl" ((id "_19") (name "syl") (stress 1)))
(("f" ((id "_20") (name "f") (end 0.86216313))))
(("ih" ((id "_21") (name "ih") (end 0.93317086))))
(("f" ((id "_22") (name "f") (end 1.0023116)))))
(("syl" ((id "_23") (name "syl") (stress 0)))
(("t" ((id "_24") (name "t") (end 1.0642071))))
(("iy" ((id "_25") (name "iy") (end 1.1534019))))))
(("three"
((id "_5")
(name "three")
(pos_index 1)
(pos_index_score 0)
(pos "cd")
(phr_pos "cd")
(pbreak_index 0)
(pbreak_index_score 0)
(pbreak "B")
(blevel 3)))
(("syl" ((id "_26") (name "syl") (stress 1)))
(("th" ((id "_27") (name "th") (end 1.2816957))))
(("r" ((id "_28") (name "r") (end 1.3449684))))
(("iy" ((id "_29") (name "iy") (end 1.5254952)))))))
festival> (utt.relation_tree utter 'IntEvent)
((("L-L%" ((id "_32") (name "L-L%"))))
(("H*" ((id "_33") (name "H*"))))
(("H*" ((id "_34") (name "H*"))))
(("H*" ((id "_35") (name "H*")))))
festival> (utt.relation_tree utter 'Intonation)
((("syl" ((id "_26") (name "syl") (stress 1)))
(("L-L%" ((id "_32") (name "L-L%")))))
(("syl" ((id "_7") (name "syl") (stress 1)))
(("H*" ((id "_33") (name "H*")))))
(("syl" ((id "_10") (name "syl") (stress 1)))
(("H*" ((id "_34") (name "H*")))))
(("syl" ((id "_19") (name "syl") (stress 1)))
(("H*" ((id "_35") (name "H*"))))))
festival> (utt.relation_tree utter 'Target)
((("t" ((id "_8") (name "t") (end 0.25016451)))
(("0" ((id "_36") (f0 101.42016) (pos 0.1)))))
(("uw" ((id "_9") (name "uw") (end 0.32980475)))
(("0" ((id "_37") (f0 121.11904) (pos 0.25)))))
(("hh" ((id "_11") (name "hh") (end 0.39506164)))
(("0" ((id "_38") (f0 119.19957) (pos 0.30000001)))))
(("ah" ((id "_12") (name "ah") (end 0.48999402)))
(("0" ((id "_39") (f0 123.81679) (pos 0.44999999)))))
(("d" ((id "_15") (name "d") (end 0.59711802)))
(("0" ((id "_40") (f0 117.02986) (pos 0.60000002)))))
(("ax" ((id "_17") (name "ax") (end 0.67743915)))
(("0" ((id "_41") (f0 110.17942) (pos 0.85000008)))))
(("f" ((id "_20") (name "f") (end 0.86216313)))
(("0" ((id "_42") (f0 108.59299) (pos 1.0000001)))))
(("ih" ((id "_21") (name "ih") (end 0.93317086)))
(("0" ((id "_43") (f0 115.24371) (pos 1.1500001)))))
(("t" ((id "_24") (name "t") (end 1.0642071)))
(("0" ((id "_44") (f0 108.76601) (pos 1.3000002)))))
(("iy" ((id "_25") (name "iy") (end 1.1534019)))
(("0" ((id "_45") (f0 102.23844) (pos 1.4500003)))))
(("th" ((id "_27") (name "th") (end 1.2816957)))
(("0" ((id "_46") (f0 99.160072) (pos 1.5000002)))))
(("iy" ((id "_29") (name "iy") (end 1.5254952)))
(("0" ((id "_47") (f0 90.843689) (pos 1.7500002))))
(("0" ((id "_48") (f0 88.125809) (pos 1.8000003))))))
festival> (utt.relation_tree utter 'HMMstate)
((("pau_1" ((id "_49") (name "pau_1") (statepos 1) (end 0.050000001)*
(("pau_2" ((id "_50") (name "pau_2") (statepos 2) (end 0.1))))
(("pau_3" ((id "_51") (name "pau_3") (statepos 3) (end 0.15000001)*
(("t_1" ((id "_52") (name "t_1") (statepos 1) (end 0.16712391))))
(("t_2" ((id "_53") (name "t_2") (statepos 2) (end 0.23217295))))
(("t_3" ((id "_54") (name "t_3") (statepos 3) (end 0.25016451))))
(("uw_1" ((id "_55") (name "uw_1") (statepos 1) (end 0.2764155))))
(("uw_2" ((id "_56") (name "uw_2") (statepos 2) (end 0.3001706))))
(("uw_3" ((id "_57") (name "uw_3") (statepos 3) (end 0.32980475))))
(("hh_1" ((id "_58") (name "hh_1") (statepos 1) (end 0.3502973))))
...
...
(("iy_1" ((id "_100") (name "iy_1") (statepos 1) (end 1.3995106))))
(("iy_2" ((id "_101") (name "iy_2") (statepos 2) (end 1.4488922))))
(("iy_3" ((id "_102") (name "iy_3") (statepos 3) (end 1.5254952))))
(("pau_1" ((id "_103") (name "pau_1") (statepos 1) (end 1.5754951)*
(("pau_2" ((id "_104") (name "pau_2") (statepos 2) (end 1.6254952)*
(("pau_3" ((id "_105") (name "pau_3") (statepos 3) (end 1.6754951)*
festival> (utt.relation_tree utter 'segstate)
((("pau" ((id "_30") (name "pau") (end 0.15000001)))
(("pau_1" ((id "_49") (name "pau_1") (statepos 1) (end 0.050000001)
(("pau_2" ((id "_50") (name "pau_2") (statepos 2) (end 0.1))))
(("pau_3" ((id "_51") (name "pau_3") (statepos 3) (end 0.15000001)*
(("t" ((id "_8") (name "t") (end 0.25016451)))
(("t_1" ((id "_52") (name "t_1") (statepos 1) (end 0.16712391))))
(("t_2" ((id "_53") (name "t_2") (statepos 2) (end 0.23217295))))
(("t_3" ((id "_54") (name "t_3") (statepos 3) (end 0.25016451)))))
(("uw" ((id "_9") (name "uw") (end 0.32980475)))
(("uw_1" ((id "_55") (name "uw_1") (statepos 1) (end 0.2764155))))
(("uw_2" ((id "_56") (name "uw_2") (statepos 2) (end 0.3001706))))
(("uw_3" ((id "_57") (name "uw_3") (statepos 3) (end 0.32980475))))
...
...
(("iy" ((id "_29") (name "iy") (end 1.5254952)))
(("iy_1" ((id "_100") (name "iy_1") (statepos 1) (end 1.3995106))))
(("iy_2" ((id "_101") (name "iy_2") (statepos 2) (end 1.4488922))))
(("iy_3" ((id "_102") (name "iy_3") (statepos 3) (end 1.5254952))*
(("pau" ((id "_31") (name "pau") (end 1.6754951)))
(("pau_1" ((id "_103") (name "pau_1") (statepos 1) (end 1.5754951)*
(("pau_2" ((id "_104") (name "pau_2") (statepos 2) (end 1.6254952)*
(("pau_3" ((id "_105") (name "pau_3") (statepos 3) (end 1.6754951)*
festival> (utt.relation_tree utter 'mcep)
((("pau_1"
((id "_106")
(frame_number 0)
(name "pau_1")
(clustergen_param_frame 19315))))
(("pau_1"
((id "_107")
(frame_number 1)
(name "pau_1")
(clustergen_param_frame 19315))))
(("pau_1"
((id "_108")
(frame_number 2)
(name "pau_1")
(clustergen_param_frame 19315))))
(("pau_1"
((id "_109")
(frame_number 3)
(name "pau_1")
(clustergen_param_frame 19315))))
...
...
(("t_1"
((id "_137")
(frame_number 31)
(name "t_1")
(clustergen_param_frame 26089))))
(("t_1"
((id "_138")
(frame_number 32)
(name "t_1")
(clustergen_param_frame 26085))))
(("t_1"
((id "_139")
(frame_number 33)
(name "t_1")
(clustergen_param_frame 26085))))
(("t_2"
((id "_140")
(frame_number 34)
(name "t_2")
(clustergen_param_frame 26642))))
...
...
(("uw_1"
((id "_157")
(frame_number 51)
(name "uw_1")
(clustergen_param_frame 27595))))
...
(("pau_3"
((id "_438")
(frame_number 332)
(name "pau_3")
(clustergen_param_frame 22148))))
(("pau_3"
((id "_439")
(frame_number 333)
(name "pau_3")
(clustergen_param_frame 22148))))
(("pau_3"
((id "_440")
(frame_number 334)
(name "pau_3")
(clustergen_param_frame 22148))))
(("pau_3"
((id "_441")
(frame_number 335)
(name "pau_3")
(clustergen_param_frame 22365)))))
festival> (utt.relation_tree utter 'mcep_link)
((("pau_1" ((id "_49") (name "pau_1") (statepos 1) (end 0.050000001).
(("pau_1"
((id "_106")
(frame_number 0)
(name "pau_1")
(clustergen_param_frame 19315))))
(("pau_1"
((id "_107")
(frame_number 1)
(name "pau_1")
(clustergen_param_frame 19315))))
(("pau_1"
((id "_108")
(frame_number 2)
(name "pau_1")
(clustergen_param_frame 19315))))
...
...
(("pau_3"
((id "_439")
(frame_number 333)
(name "pau_3")
(clustergen_param_frame 22148))))
(("pau_3"
((id "_440")
(frame_number 334)
(name "pau_3")
(clustergen_param_frame 22148))))
(("pau_3"
((id "_441")
(frame_number 335)
(name "pau_3")
(clustergen_param_frame 22365))))))
festival> (utt.relation_tree utter 'Wave)
((("0" ((id "_442") (wave "[Val wave]")))))
festival>
Notes :
* some parentheses have been deleted in the display for formating reasons
… some content has been deleted to reduce the size of the analyzed code
Results of the code analysis
The number of items created for the string “253” are shown in the following table :
| number |
item |
id’s |
| 1 |
token |
1 |
| 4 |
word |
2-5 |
| 1 |
phrase |
6 |
| 6 |
syllable |
7, 10, 14, 19, 23, 26 |
| 19 |
segment |
8-9, 11-13, 15-18, 20-22, 24-25, 27-31 |
| 4 |
intevent |
32-35 |
| 13 |
target |
36-48 |
| 57 |
hmmstate |
49-105 |
| 336 |
mcep |
106-441 |
| 1 |
wave |
442 |
The features associated to the different items are presented in the next table :
| item |
features |
| token |
name, whitespace, prepunctuation, token_pos |
| word |
name, pos_index, pos_index_score, pos, phr_pos, phrase_score, pbreak_index, pbreak_index_score, pbreak, blevel |
| phrase |
name |
| syllable |
name, stress |
| segment |
name, end |
| intevent |
name |
| target |
f0, pos |
| hmmstate |
name, statepos, end |
| mcep |
name, frame_number, clustergen_param_frame |
| wave |
Val |
The last table shows the relations between the different items in the HRG :
| item |
daughter |
leaf |
relation |
| token |
word |
x |
Token |
| word |
syllable |
– |
SylStructure |
| phrase |
word |
x |
Phrase |
| syllable |
segment |
x (except silence) |
SylStructure |
| syllable |
intevent |
x |
Intonation |
| segment |
target |
x |
Target |
| segment |
hmmstate |
x |
segstate |
| segment |
mcep |
x |
mcep_link |
Relations between utterance items
To better understand the relations between utterance items, I use a second example :
festival>
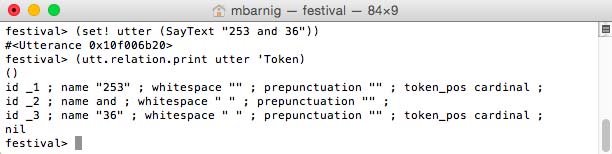
(set! utter (SayText "253 and 36"))
(utt.relation.print utter 'Token)
Festival SayText
There are 3 tokens. The Token relation is a list of trees where each root is the white space separated tokenized object from the input character string and where the daughters are the list of words associated with the tokens. Most often it is a one to one relationship, but in the case of digits a token is associated with several words. The following command shows the Token tree with the daughters :
(utt.relation_tree utter 'Token)
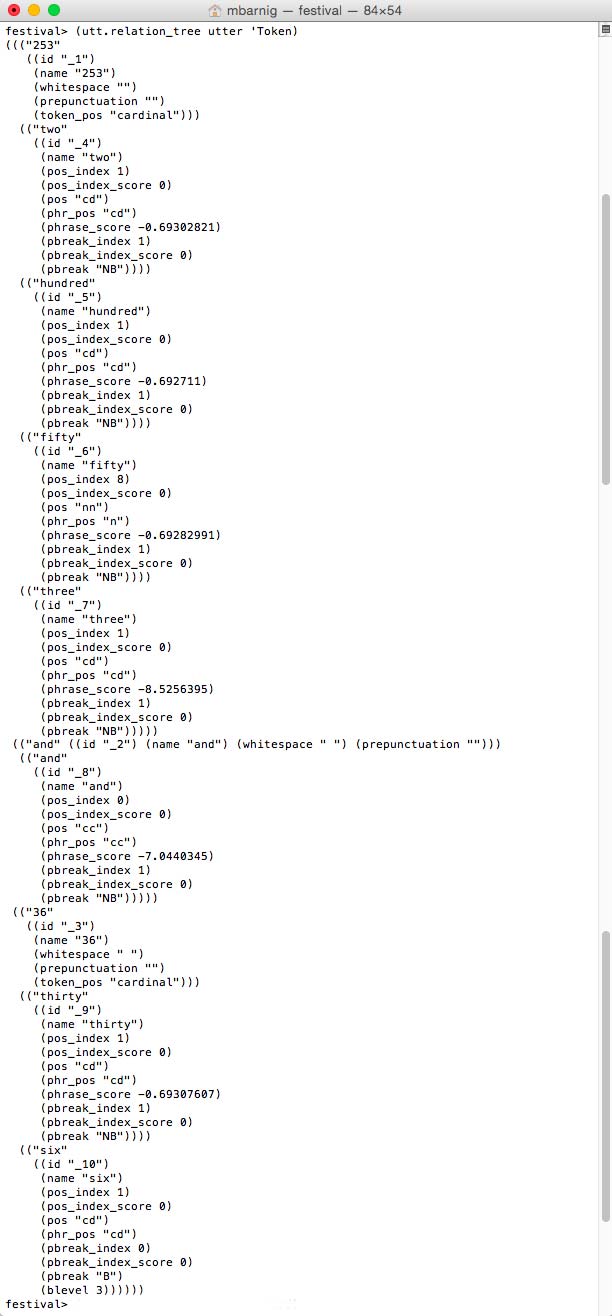
Festival Token_tree
We can check that the word list corresponds to the Token tree list :
(utt.relation.print utter 'Word)
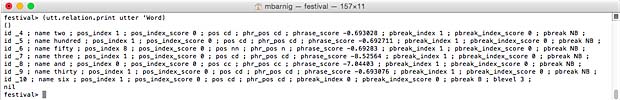
Festival Word List
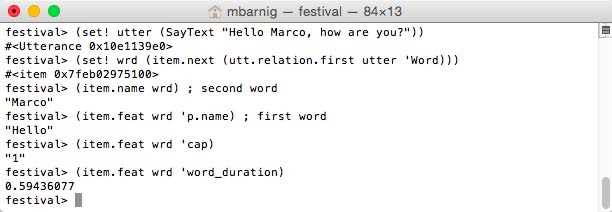
To access the second word of the first token we can use two methods :
(item.name (item.daughter2 (utt.relation.first utter 'Token)))
or
(item.name (item.next (utt.relation.first utter 'Word)))
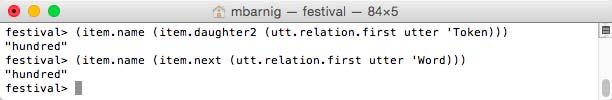
Festival access methods to word item
TTS stages and steps
In the next chapters the different stages and steps executed to synthesize a text string are described with more details. In the first step a simple and a complex utterance of type Text are created :
(set! simple_utt (Utterance Text
"The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"))
(set! complex_utt (Utterance Text
"Mr. James Brown Jr. attended flight No AA4101 to Boston on
Friday 02/13/2014."))
The complex utterance named complex_utt is used in the following examples.
1. Text-to-Token Conversion
Text
Text is a string of characters in ASCII or ISO-8850 format. Written (raw) text usually contains also numbers, names, abbreviations, symbols, punctuation etc which must be translated into spoken text. This process is called Tokenization. Other terms used are (lexical) Pre-Processing, Text Normalization or Canonicalization. To access the items and features of the defined utterance named complex_utt in Festival we use the following modules :
festival> (Initialize complex_utt) ; Initialize utterance
festival> (utt.relationnames complex_utt) ; show created relations
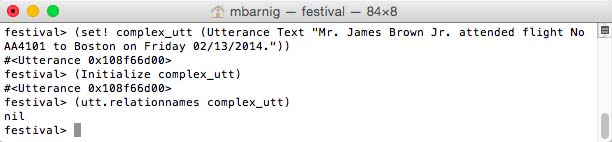
Festival Utterance Initialization
The result nil indicates that there exist not yet a relation inside the text-utterance.
Tokens
The second step is the Tokenization which consists in the conversion of the input text to tokens. A token is a sequence of characters where whitespace and punctuation are eliminated. The following Festival command is used to convert raw text to tokens and to show them :
festival> (Text complex_utt) ; convert text to tokens
festival> (utt.relationnames complex_utt) ; check new relations
festival> (utt.relation.print complex_utt 'Token) ; display tokens
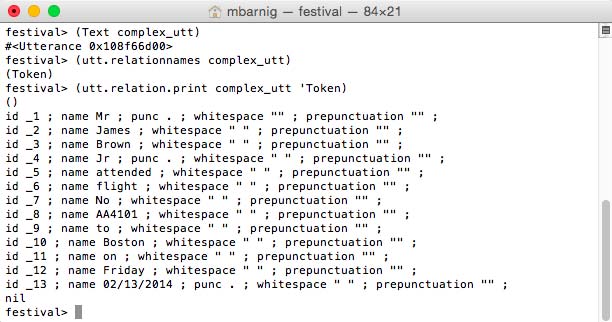
Festival Text Module to convert raw text to tokens
There are several methods to access individual tokens :
festival> (utt.relation.first complex_utt 'Token) ; returns 1st token
festival> (utt.relation.last complex_utt 'Token) ; returns last token
festival> (utt.relation_tree complex_utt 'Token) ; returns token tree
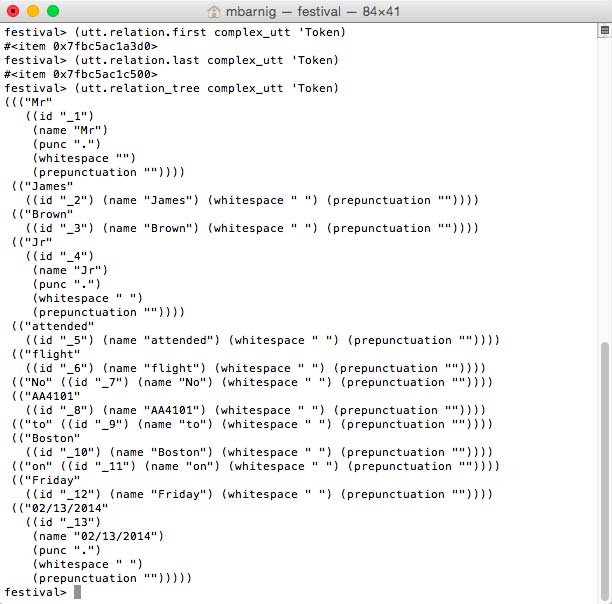
Festival Token Access
This utt.relation_tree method can also be applied to other relations than ‘Tokens.
2. Token-to-Word Conversion
Words
In linguistics, a word is the smallest element that may be uttered in isolation with semantic or pragmatic content. To convert the isolated tokens to words, we use the Festival commands :
festival> (Token complex_utt) ; token to word conversion
festival> (utt.relationnames complex_utt) ; check new relations
festival> (utt.relation.print complex_utt 'Word) ; display words
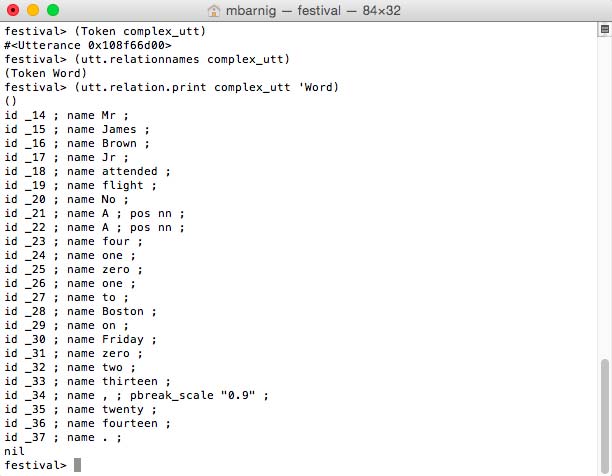
Festival Token Module to convert tokens to words
The rules to perform the token to word conversion are specified in the Festival script token.scm.
POS
Part-of-Speech (POS) Tagging is related to the Token-to-Word conversion. POS is also called grammatical tagging or word-category disambiguation. It’s the process of marking up a word in a text as corresponding to a particular part of speech, based on both its definition, as well as its context (identification of words as nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, etc.)
To do the POS tagging, we use the commands
festival> (POS complex_utt) ; Part of Speech tagging
festival> (utt.relationnames complex_utt) ; check new relations
festival> (utt.relation.print complex_utt 'Word) ; display words
The relation check shows that no new relation was created with the POS method. There are however new features which have been added to the ‘Word relation.
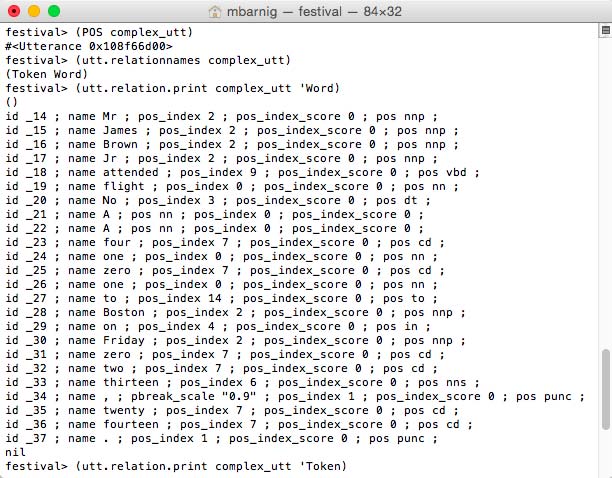
Festival POS Module to tag the words
The new features are :
- pos_index n
- pos_index_score m
- pos xx
Phrase
The last step of the Token-to-Word conversion is the phrasing. This process determines the places where phrase boundaries should be inserted. Prosodic phrasing in TTS makes the whole speech more understandable. The phrasing is launched with the following commands :
festival> (Phrasify complex_utt) ;
festival> (utt.relationnames complex_utt) ; check new relations
festival> (utt.relation.print complex_utt 'Phrase) ; display breaks
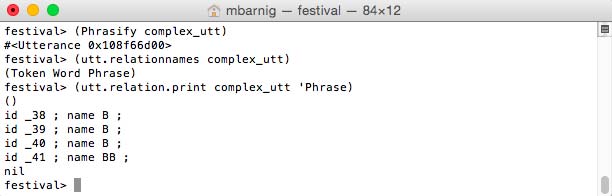
Festival Phrasify Module to insert boundaries
The result can be seen in new attributes in the Word relation:
festival> (utt.relation.print complex_utt 'Word)
- phr_pos xx
- phrase_score nn
- pbreak_index n
- pbreak_index_score m
- pbreak yy (B for small breaks, BB is for big breaks, NB for no break)
- blevel p
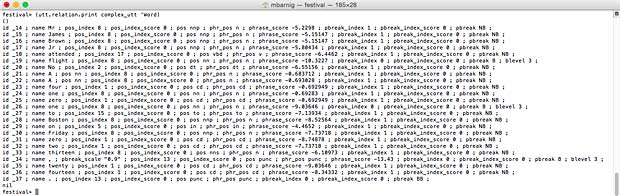
Festival Word list after phrasing (click to enlarge)
3. Word-to-Phoneme Conversion
The command
festival> (Word complex_utt)
generates 3 new relations : syllables, segments and SylStructure.
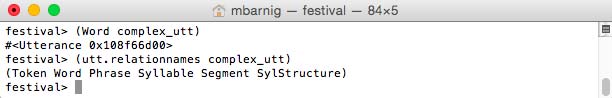
Festival relations generated by the Word method
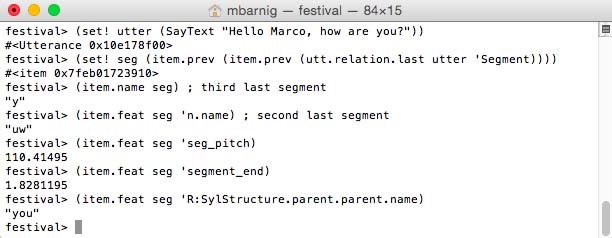
Segment
Segments and phones are synonyms.
festival> (utt.relation.print complex_utt 'Segment)
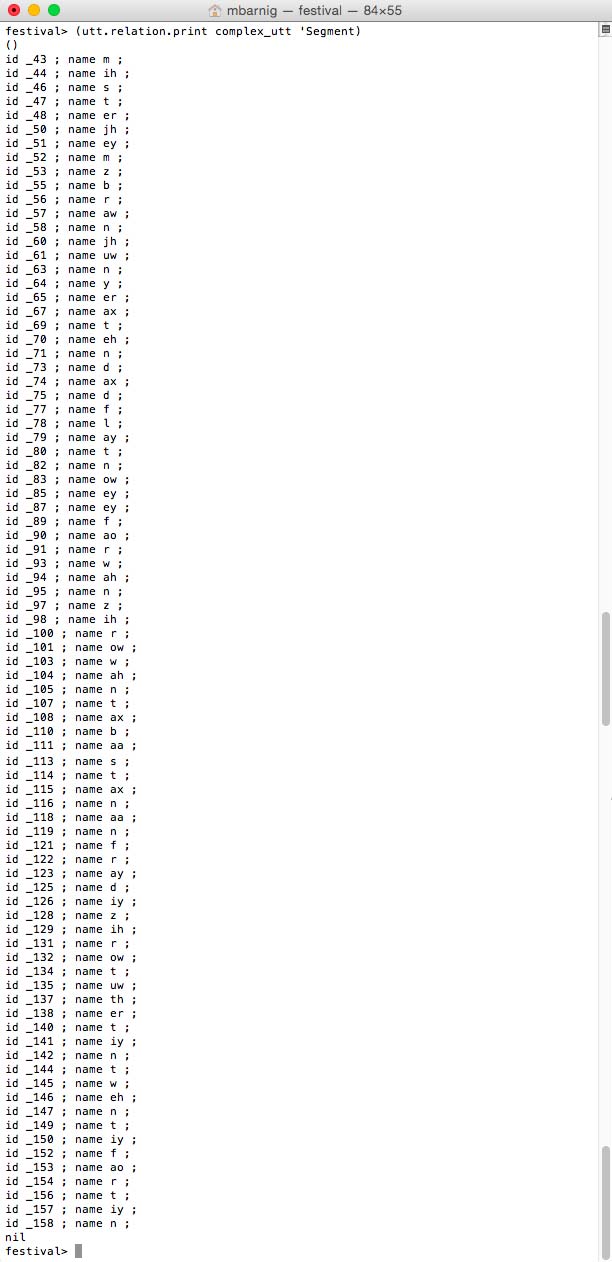
Festival segments = phones
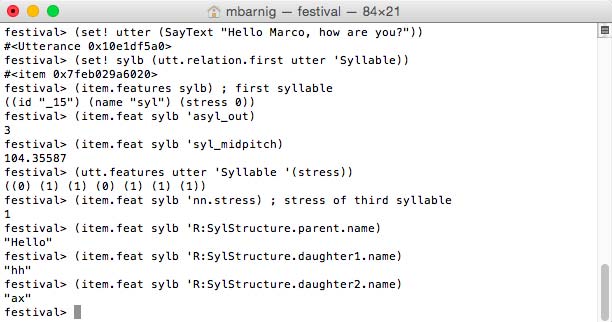
Syllable
Consonants and vowels combine to make syllables. They are often considered the phonological building blocks of words, but there is no universally accepted definition for a syllable. An approximate definition is : a syllable is a vowel sound together with some of the surrounding consonants closely associated with it. The general structure of a syllable consists of three segments :
- Onset : a consonant or consonant cluster
- Nucleus : a sequence of vowels or syllabic consonant
- Coda : a sequence of consonants
Nucleus and coda are grouped together as a Rime. Prominent syllables are called accented; they are louder, longer and have a different pitch.
The following Festival command shows the syllables of the defined utterance.
festival> (utt.relation.print complex_utt 'Syllable)
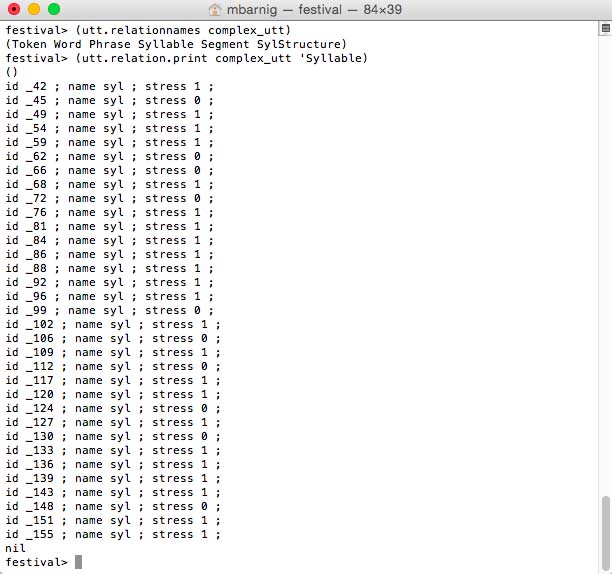
Festival syllables
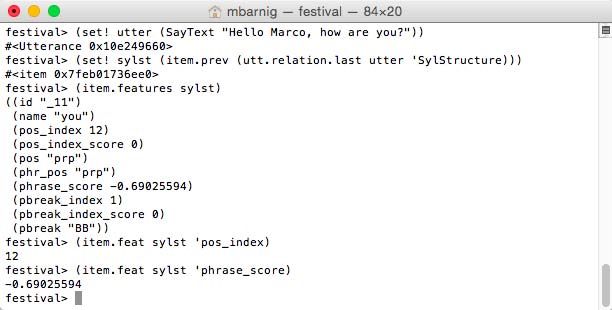
SylStructure
Words, segments and syllables are related in the HRG trought the SylStructure. The command
festival> (utt.relation.print complex_utt 'SylStructure)
prints these related items.
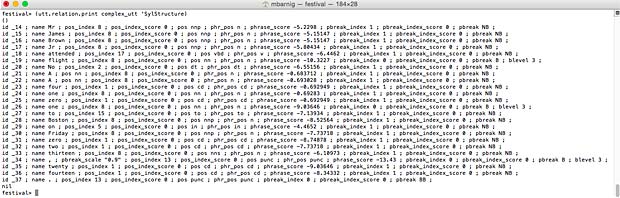
Festival SylStructure (click to enlarge)
4. Prosodic Information Addition
Besides the phrasing with break indices, additional prosodic components can be added to speech synthesis to improve the voice quality. Some of these elements are :
- pitch accents (stress)
- final boundary tones
- phrasal tones
- F0 contour
- tilt
- duration
Festival supports ToBI, a framework for developing community-wide conventions for transcribing the intonation and prosodic structure of spoken utterances in a language variety.
The process
festival> (Intonation complex_utt)
generates two additional relations : IntEvent and Intonation
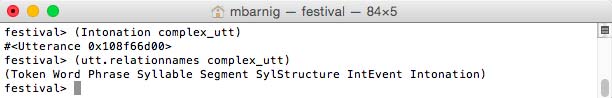
Festival prosodic relations
IntEvent
The command
festival> (utt.relation.print complex_utt 'IntEvent)
prints the IntEvent items.
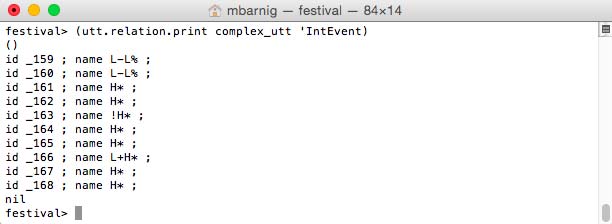
Festival IntEvent items
The following types are listed :
- L-L% : low boundary tone
- H* : peak accent
- !H* : downstep high
- L+H* : bitonal accent, rising peak
Intonation
The command
festival> (utt.relation.print complex_utt 'Intonation)
prints the Intonation items.
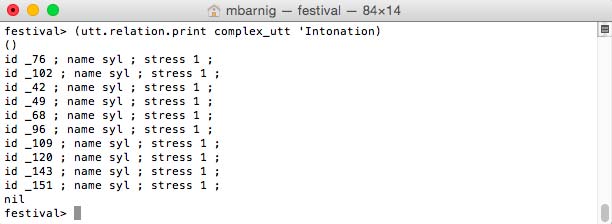
Festival Intonation items
Only the syllables with stress are displayed.
Duration
The process
festival> (Duration complex_utt)
creates no new relations and I have not seen any new items or features in other relations.
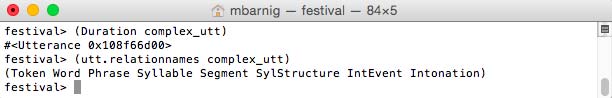
utt14
Target
The last process in the prosodic stage
festival> (Int_Targets complex_utt)
generates the additional relation Target.
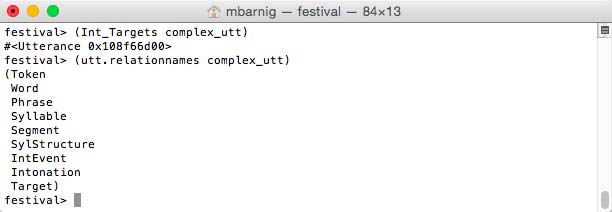
Festival relations after the Int_Targets process
The command
festival> (utt.relation.print complex_utt 'Target)
prints the target items.
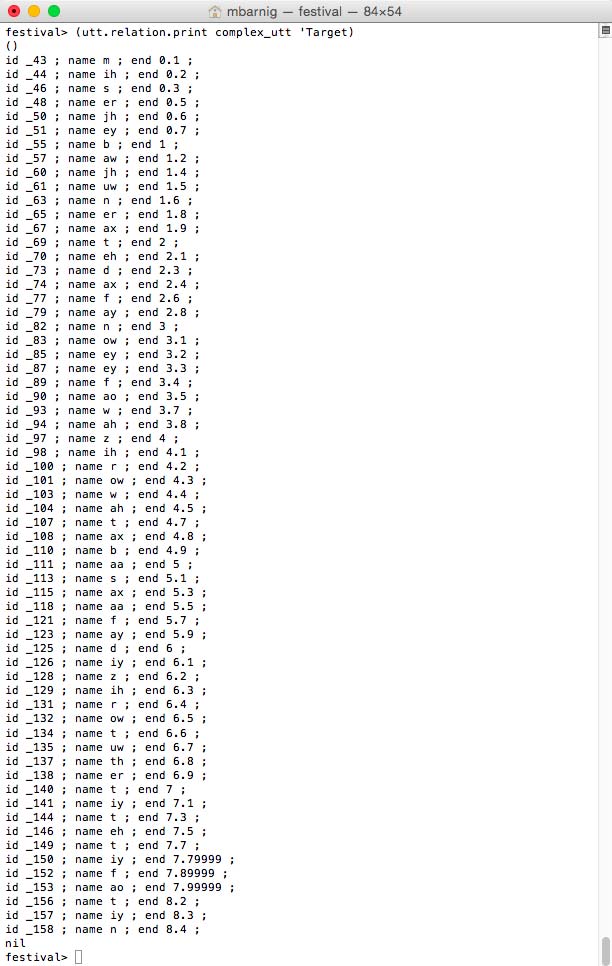
Festival clustergen targets
The unique target features are the segment name and the segment end time.
5. Waveform Generation
Wave
The process
festival> (Wave_Synth complex_utt)
festival> (utt.relation.print complex_utt 'Wave)
generates five new relations :
- HMMstate
- segstate
- mcep
- mcep_links
- Wave
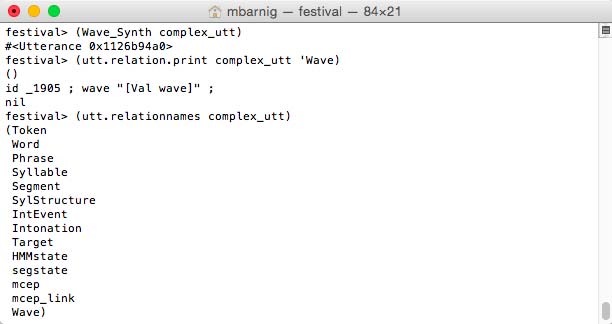
Festival Wave relations for clustergen voice
In the next chapters we use the method
(utt.relation.print complex_utt 'Relation)
to display the relations and features specific to the diphone voice.
Relation ‘HMMstate
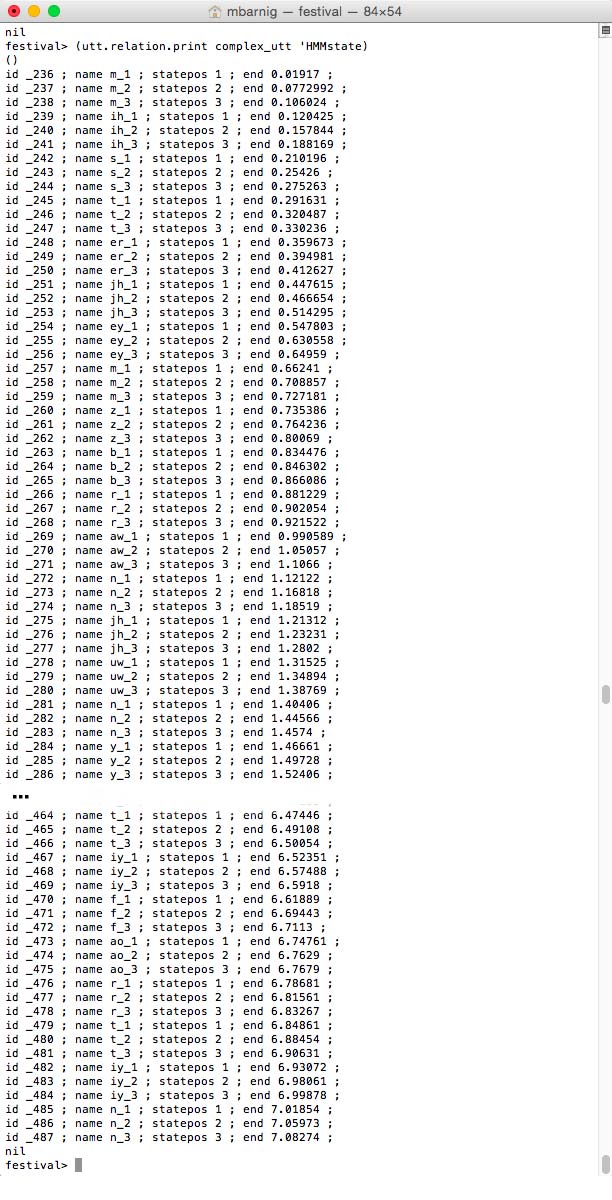
HMMstates for Festival clustergen voice
Relation ‘segstate
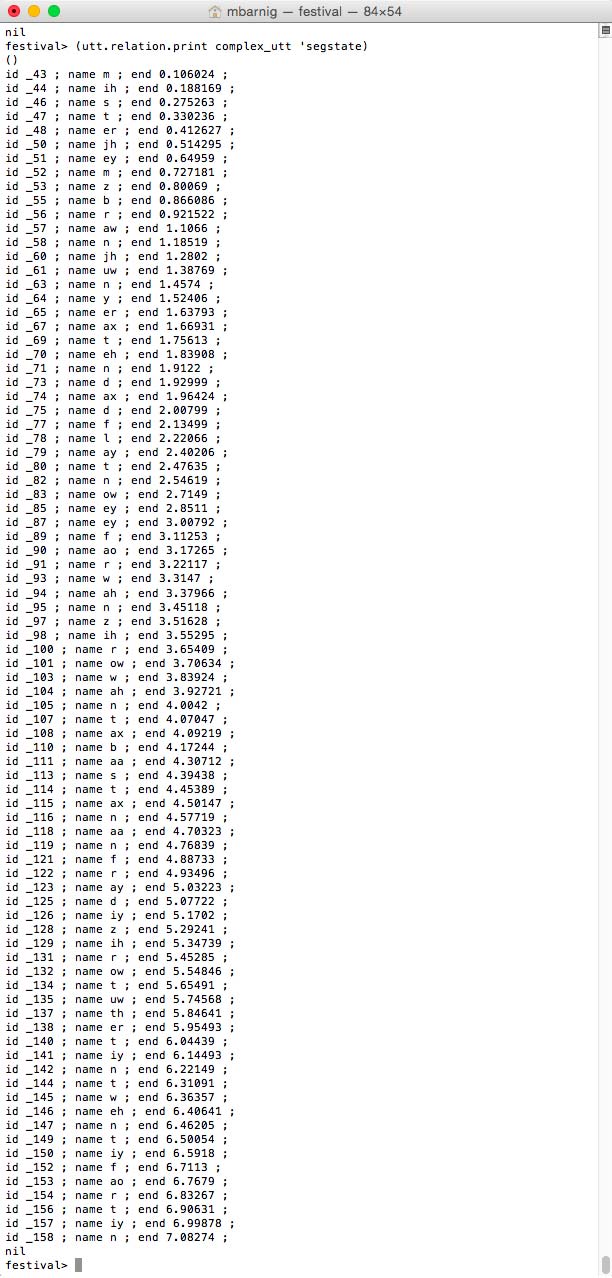
segstates for Festival clustergen voice
Relation ‘mcep
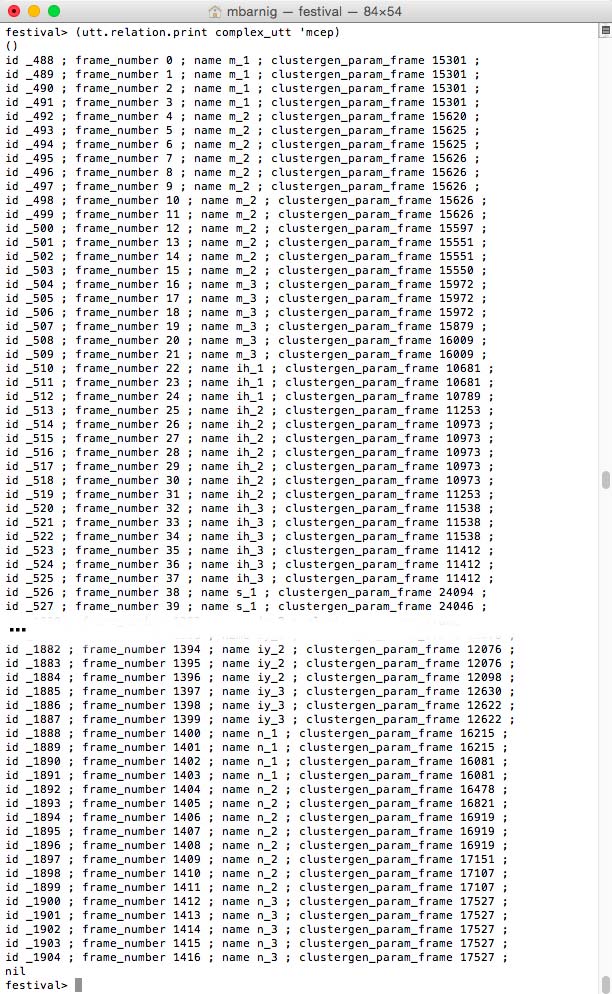
mcep features for Festival clustergen voice
Relation ‘mcep_links

mcep_links relation for Festival clustergen voice
Relation ‘Wave
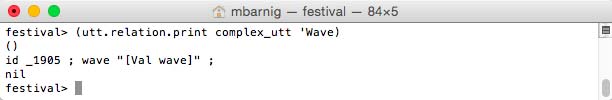
Wave relation for Festival clustergen voice
Diphone Voice Utterance
If we use a diphone voice (e.g. the default kal_diphone voice) instead of the clustergen voice, the last step of the prosodic stage (No 4) and the complete wave-synthesis stage (No 5) provide different relations and features.
We use the Festival method “SayText”, a combination of the above presented processes
- Initialize utt
- Text utt
- Token utt
- POS utt
- Phrasify utt
- Word utt
- Intonation utt
- Duration utt
- Int_Targets utt
- Wave_Synt utt
to create the same complex utterance as in the first example :
festival>
(set! complex_utt (SayText "Mr. James Brown Jr. attended flight
No AA4101 to Boston on Friday 02/13/2014."))
(utt.relationnames complex_utt)
Here are the results :
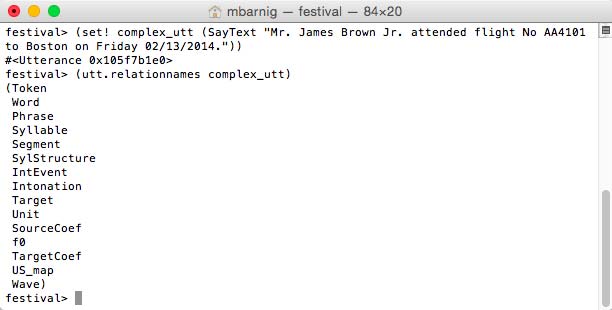
Utterance relations for a Festival diphone voice
In the next chapters we use the method
(utt.relation.print complex_utt 'Relation)
to display the relations and features specific to the diphone voice.
Relation ‘Target
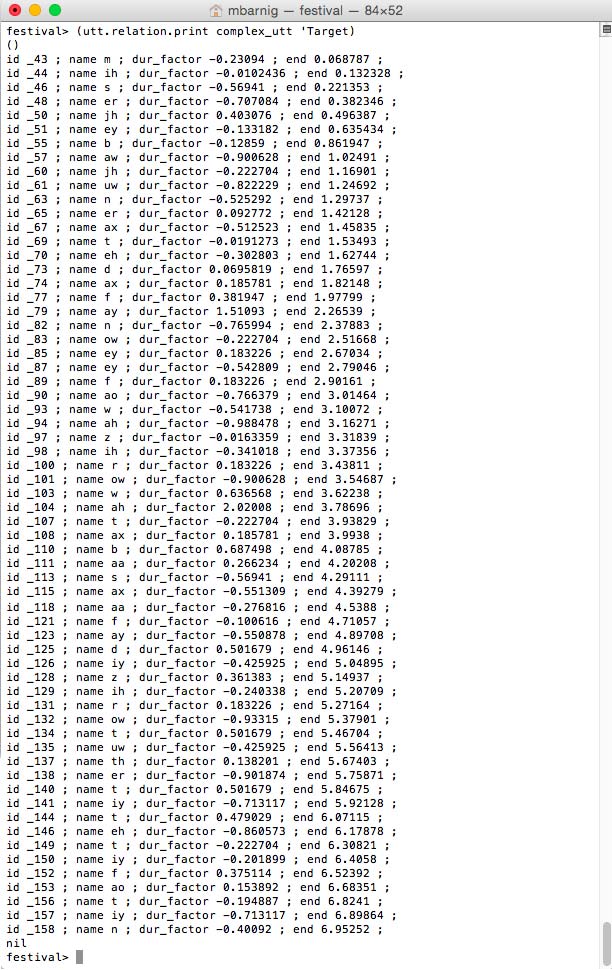
Relation Target for diphone voice
Relation ‘Unit

Relation Unit for diphone voice (click to enlarge)
Relation ‘SourceCoef
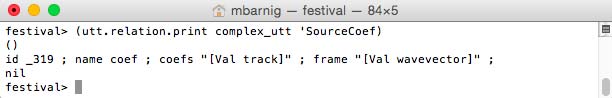
Relation ‘SourceCoef for diphone voice
Relation ‘fo
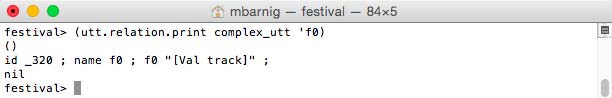
Relation f0 for diphone voice
Relation ‘TargetCoef
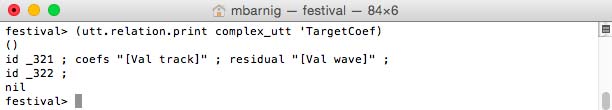
Relation TargetCoef for diphone voice
Relation ‘US_map
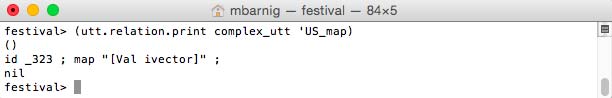
Relation US_map for diphone voice
Relation ‘Wave
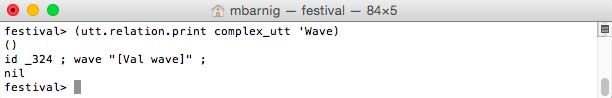
Relation Wave for diphone voice
Playing and saving the diphone voice utterance :
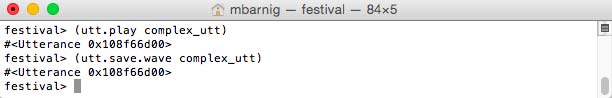
Playing and saving a synthesized Festival utterance
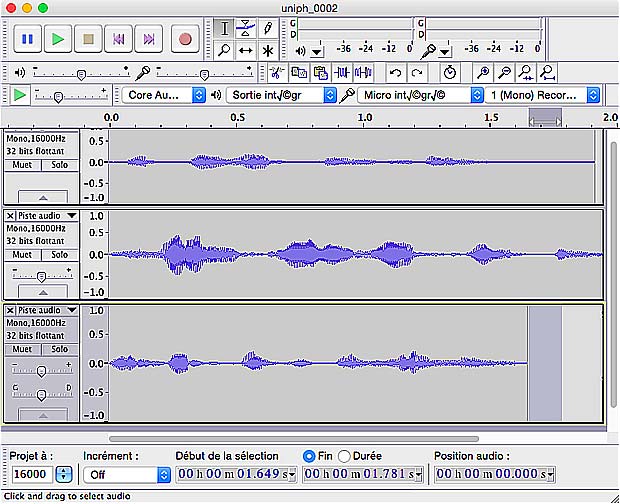
Diphone voice utterance shown in Audacity :
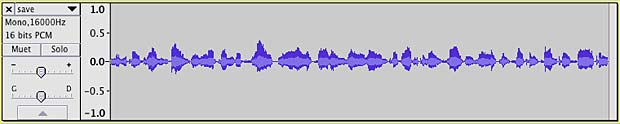
Display of a synthesized Festival utterance
Clunits Voice Utterance
What is true for the diphone voice is also ture for a clunits voice. The last step of the prosodic stage (No 4) and the complete wave-synthesis stage (No 5) generate different relations and features. As an example we use a swedish clunits voice :
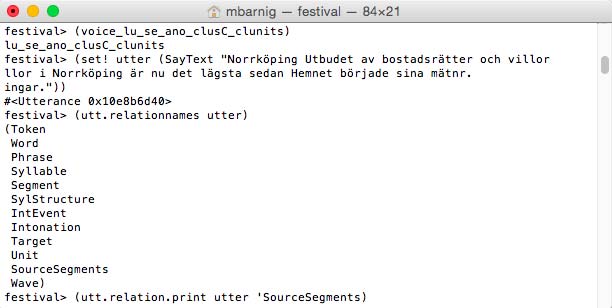
Relations for Festival clunits voice
Relation ‘Target
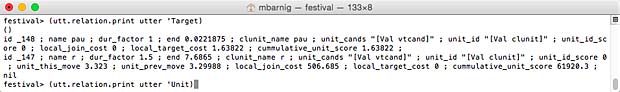
Relation Target for Festival clunits voice (click to enlarge)
Relation ‘Unit
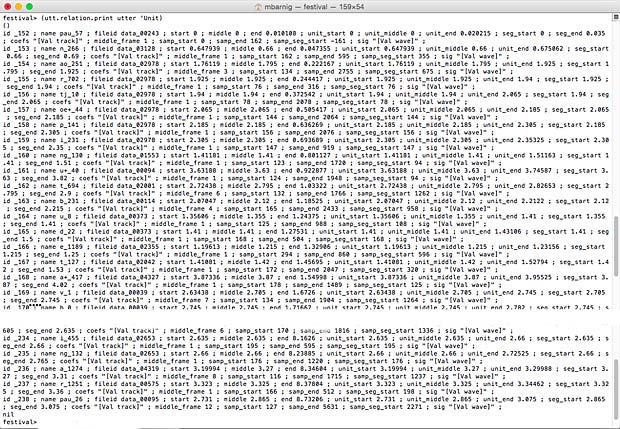
Relation unit for Festival clunits voice (click to enlarge)
Relation ‘SourceSegments
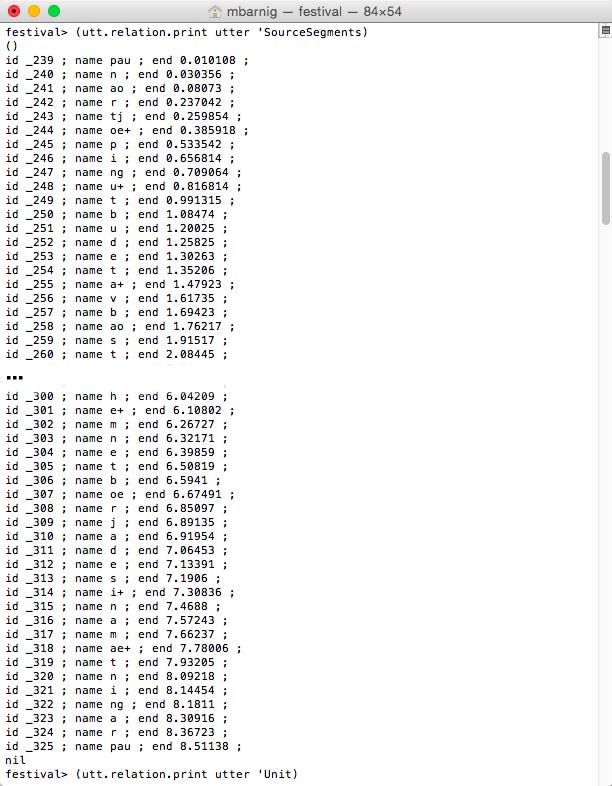
Relation SourceSegments for Festival clunits voice
That’s all.